Packing more power into smaller spaces is a common goal for equipment designers. In today’s industrial landscape, manufacturers are always seeking to improve efficiency and productivity while reducing operating costs. Components that are powerful, compact in size, and able to deliver the same capabilities as larger and more complex products are in high demand. This is especially true for actuators used on outdoor equipment such as snow ploughs and utility task vehicle (UTV) dump beds. For motion control in such applications, designers have traditionally chosen between hydraulic and electromechanical technologies but have had to accept some trade-offs for each. However, there is now a hybrid solution that offers the best features of both technologies without the drawbacks.
High load handling
Hydraulic systems amplify force according to Pascal’s law, which states that any pressure applied to a contained fluid is distributed equally throughout that fluid. This enables a relatively small force to be multiplied many times throughout a system, giving hydraulic force its ability to handle high loads.
But directing that fluid to do real work in hydraulic cylinder-based systems requires a complex assembly of hoses, pumps, valves and reservoirs, which can be noisy and costly to install, operate and maintain. Adding to this are extensive fluid-handling, storage and leakage issues, which increase maintenance costs and jeopardise workplace cleanliness. Moreover, hydraulic cylinders do not adapt well for digital control.
Clean and compact
Electromechanical systems derive power from a motor, converting electrical energy into mechanical motion. Electromechanical actuators using electrical energy do not require the complex, space-consuming and messy support structures of hydraulic cylinders, and because the current can be controlled infinitesimally, they are much more suited to today’s digital systems. As such, system designers are increasingly specifying electromechanical technologies over hydraulics.
Electromechanical actuators have had drawbacks as well. Although they can move heavy loads of more than 1600 kg, this capability has required a larger envelope. Furthermore, they are more sensitive to shock loading, which can be encountered when an overloaded trailer shifts its load while being towed. Such high shock loading can break the gearing or bend the ball screw or extensions tube of a conventional electromechanical actuator — especially if the shock happened while the actuator was fully extended.
Handling high loads without the mess and overhead
For many applications, designers can now enjoy the power of Pascal’s law in a compact footprint that can also withstand shock loading, all at a lower cost. Electro-hydraulic actuators contain powerful hydraulic systems in a housing similar to that used in a conventional electromechanical actuator.
Figure 1 illustrates the inner workings of an electro-hydraulic actuator in an extension cycle. An electric motor rotates clockwise, turning the gears which pressurise the hydraulic fluid. Valves open to draw fluid from both the reservoir and head side, and control delivery to extend the rod. On retraction, the motor runs counter clockwise, reversing the operation, and returning the fluid to the reservoir and the opposite side of the piston.
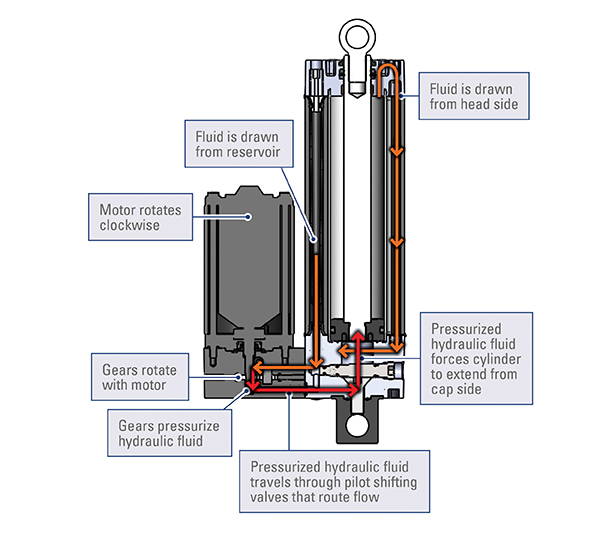
Figure 1: Extension cycle Thomson H-Track electro-hydraulic actuator
Replacing the gear and screw assemblies of conventional electromechanical actuators with a compact hydraulic system allows for handling greater loads — up to 2150 kg –– within a comparably sized envelope.
This architecture enables electro-hydraulic actuators to withstand shock loads by redistributing the fluids throughout the internal channels, thus absorbing the energy.
Compressed cycle times
In addition to high-density load handling and shock resistance, electro-hydraulic actuators can achieve higher total cycle speeds. Unlike conventional electromechanical actuators, which run at a relatively constant speed regardless of load, electro-hydraulic actuators run at high speeds at low loads, and lower speeds at high loads. If a high percentage of total cycle time is at less than full load, there is potential for a decreased overall cycle time.
The load on an actuator controlling the dump bed of a UTV, for example, might be 2150 kg initially and thus limited to a slow speed of about 6 mm per second. As the bed raises, the leverage of the actuator increases and material falls from the bed, decreasing the load on the actuator and increasing the speed to around 100 mm per second. With a conventional actuator, the speed while raising the dump bed would remain relatively constant, resulting in longer total cycle time.
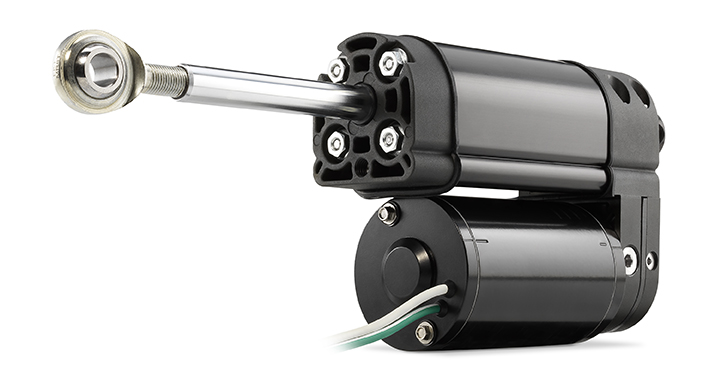
The Thomson H-Track electro-hydraulic actuator provides the performance of hydraulics without the expansive space requirements nor the prohibitive cost of full-sized hydraulic systems. It handles force up to 2150 kg, provides travel speeds near 100 mm per second and features the smallest mounting envelope in its class.
Applications abound
High power density and shock load resistance, and shorter cycle times can be beneficial in a wide range of applications, including the dump beds mentioned above, agricultural sprayers, snow ploughs, mower lift decks and many others.
Snow ploughs. When a moving plough blade strikes a stationary concrete obstacle, it can produce a sudden jarring that would destroy most linear actuators. Hybrid actuators cushion these types of blows and continue operating as required. As a result, equipment designers are able to save on replacement costs.
Larger agricultural sprayers. Agricultural sprayers are increasingly designed with larger boom lengths, reaching 40 m in the U.S. and more than 50 m in Europe, which increase cost efficiencies in the field. Large sprayer booms use actuators to fold them into a stowed position for transport, which puts very high loads on the actuators. Also, the bouncing of the booms during transport subjects the actuators to moment force. Such forces could destroy conventional actuators quickly, but electro-hydraulic actuators can handle them with ease.
Mower deck lifts. As mower decks grow larger and incorporate new innovations for faster mowing, traditional actuators are fast exceeding their limits for these applications. Hybrid actuators offer more reliable load holding, higher durability and capability to withstand higher transport speeds and high-pressure wash-downs.
Other examples. Electro-hydraulic technologies can be of benefit in many other applications, including:
- Turf care, and lawn and gardening, including golf course sweepers, sleeve hitch kits, blade lifts, and mid-mount implement lifts.
- Marine applications such as hatch lifts, transom actuators and mud motor lifts.
- Material handling applications such as pallet lifts, lift tables, conveyor deflectors and scissor tables.
- UTV/truck applications such as tailgate locks, UTV ploughs and bed lift dump boxes.
- Construction applications such as pavers, quick-attach bucket releases and plough/blade positioning.
With high power density and shock load resistance, and shorter cycle times, the Thomson H-Track electro-hydraulic actuator can be applied to a variety of material handling applications such as pallet lifts.
The right fit
Electro-hydraulic actuators are designed for extreme applications requiring high load capacity in a small footprint. Like conventional electromechanical actuators, they are cleaner and quieter than traditional hydraulic systems and do not require a complex, space- and maintenance-consuming support infrastructure of hosing, valves and other external assemblies. However, unlike conventional electromechanical actuators, they are capable of withstanding shock loads and offer the potential to reduce cycle times. Any application that requires high power density or shock resistance, or integration with digital control systems is a candidate for electro-hydraulic actuation.