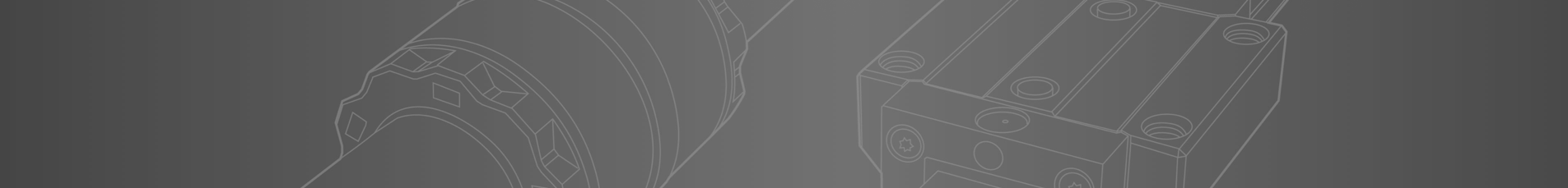
As Industry 4.0 initiatives bring more and more industrial axes of motion into the realm of automation, the need for cost-effective control across them grows as well. Advances in robotics, connectivity, cloud computing, artificial intelligence, data analysis, mobility and numerous other areas are converging to push global industry to new plateaus of operational efficiency and creating roles for actuators in places previously thought impractical.
Consider, for example, industrial tasks such as raising or lowering a conveyor to handle cartons of various sizes. If such adjustments are needed only a few times a day, automation with conventional technology would be difficult to justify. Automating such intermittent operations with pneumatic cylinders, for instance, would require a costly infrastructure and elevated maintenance costs while providing only limited control capability. Systems involving high-duty, high-precision linear actuators would provide the control needed but also far more additional capability than would be cost-justifiable for intermittent operations. Traditional industrial linear actuators would offer the right control capability at a lower cost, but even these would be difficult to justify because of the additional relay and other infrastructure necessary. Today’s smart electromechanical actuators, however, enable designers to automate intermittent operations affordably by embedding functionality that has previously required an external infrastructure.
Lower-cost actuators with embedded smart capabilities can be beneficial for intermittent applications in industrial automation plants. The actuators offer flexibility, cost efficiency and intelligence.
Smart actuators come of age
Smart linear actuators contain everything needed to switch the final element. Only two wires transmit power, and a few others communicate with a controller. This enables simple and efficient automated control of previously manually operated axes. System designers can program low-voltage switching directly into the actuator, eliminating the need for the operator to know what and when to switch.
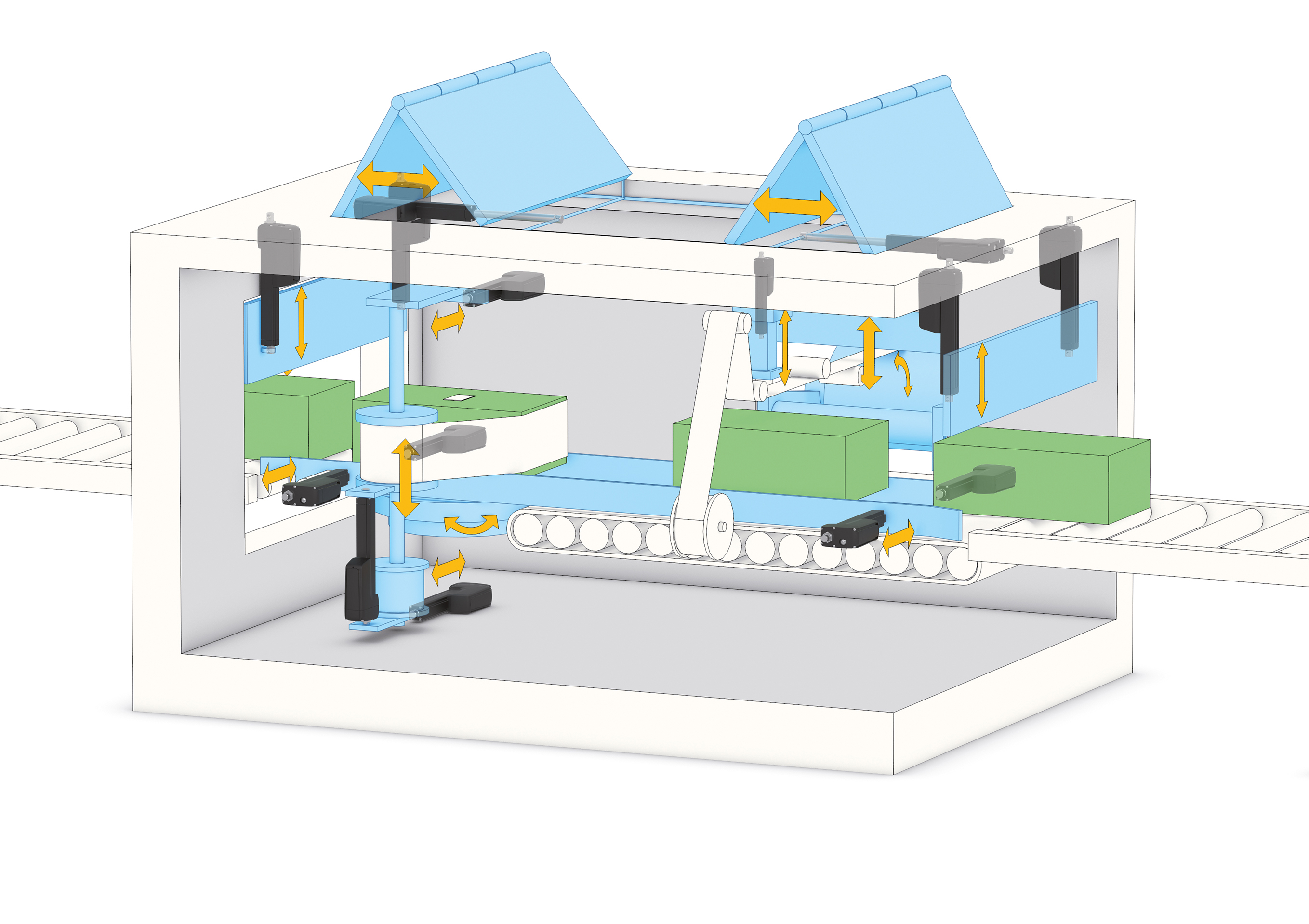
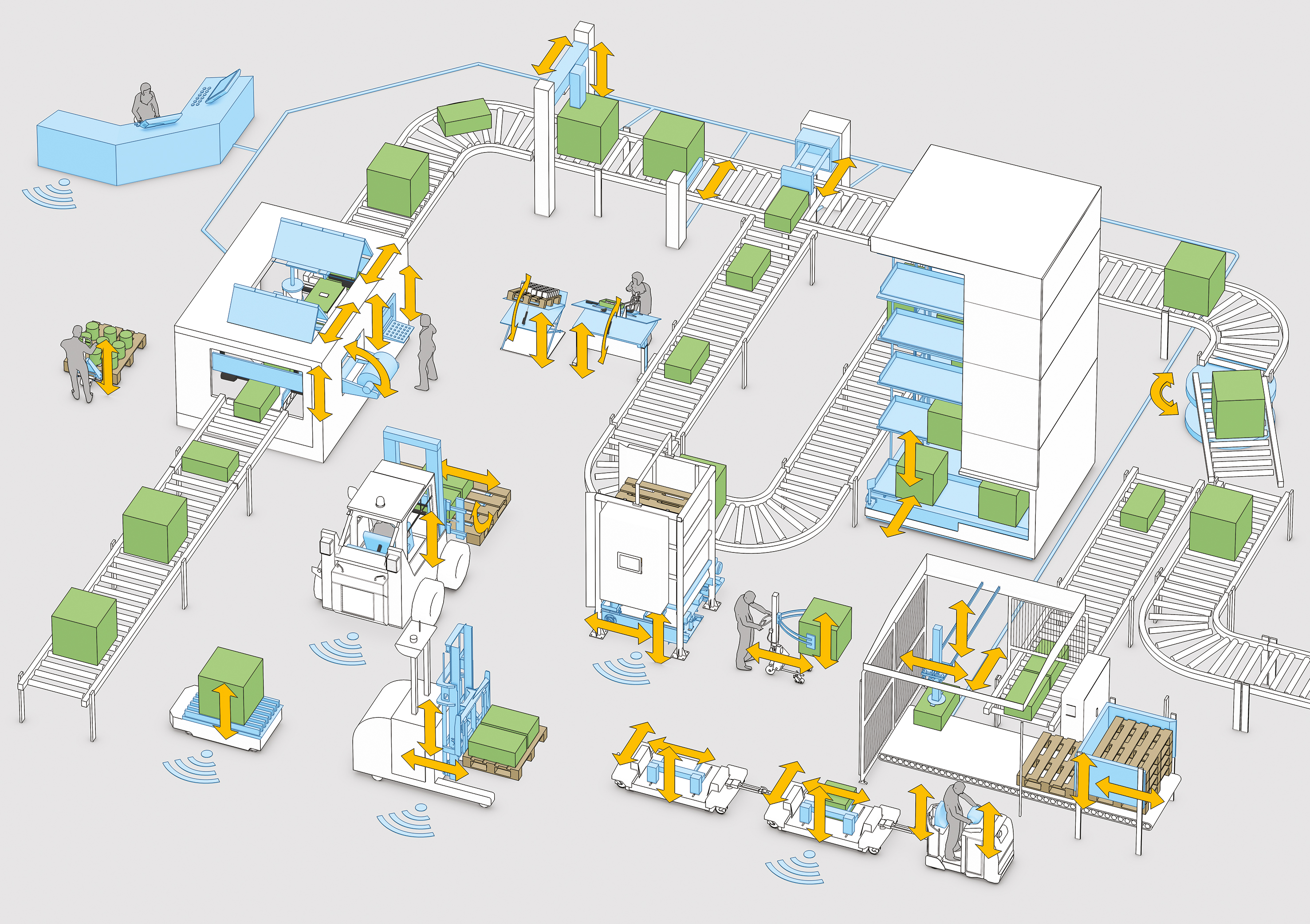
Smart actuators are widely used in various plants where manual intervention can be avoided. For example, system designers can now program the actuators in advance to perform an automated switch in control conveyors. The actuators also provide controllability for logistic trains and automated guided vehicles.
Even if automating functions such as conveyor operation do not show significant payback, the ability to participate in a larger community of connected devices can have value. Embedding networking logic into inexpensive actuators enables connection with network buses such as a CAN Bus, PROFINET or Ethernet/IP. Previous manual activities can now integrate with larger and more complicated control schemes and workflow strategies. Actuators can share vast amounts of operating data with systems such as counting technology, which can signal the precise moment to change an instruction.
Or imagine integration of smart actuators with automated guided vehicles (AGVs) that move around the plant, receiving goods from conveying stations and transporting them to other stages of production or delivery. The AGV could approach the conveyor, signal the actuator to open the hatch containing only the blue boxes, fill to capacity and move to the next station. Such integration would not likely have been feasible – or even considered – prior to Industry 4.0 innovation.
Smarter maintenance
Smart actuators can also monitor their own health. They know whether the system is receiving enough voltage for the job at hand and may be able to adjust accordingly. They can accumulate data on the number of cycles performed and pace operation across shifts. And they can communicate absolute position at every point in the stroke, which can be programmed to push more current as needed to manage the load.
Although smart actuators themselves require little if any maintenance, they can reduce overall maintenance costs by recognising load variations that impact actuator wear and helping synchronise replacement with planned machine downtime accordingly.
Driving innovation
The potential to connect devices that have previously been out of reach is wide open, and geography is no longer a barrier to industrial automation and integration. The stage is set for production and automation engineers to define the actuator applications that will shape the next generation of industrial innovation.